Why Is Group 14 Called the Carbon Family
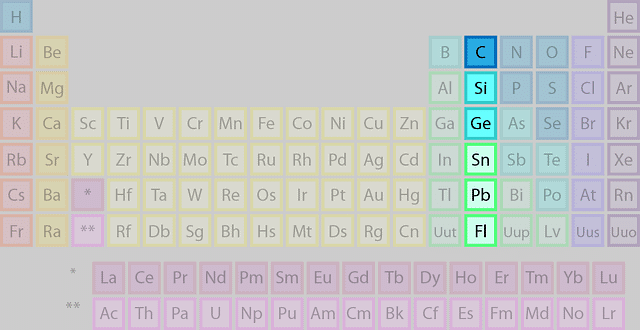
The grouping 14 elements are the 2nd group in the p-block of the periodic table. It is also called the carbon group. The members of this group are:
- Carbon (C)
- Silicon (Si)
- Germanium (Ge)
- Can (Sn)
- Pb (Lead)
- Flerovium (Fl)
Endeavour yourself:Which of the following elements does non belong to the Carbon family?
Caption
The elements of the Carbon family are the elements of group fourteen. They are carbon, Silicon, Germanium, stannum and plumbum. Their valence shell configuration is nsiinp2 and their valency is 4. Just aluminium belongs to group 13.
-
Electronic configuration: Their valence shell electronic configuration is nstwo np2.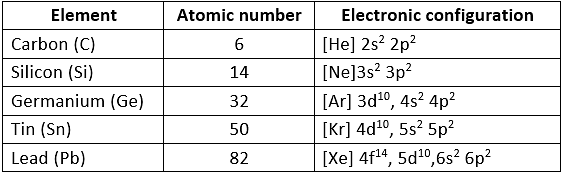
-
Metallic character: C and Si are non-metals, Ge is a metalloid and Sn and Pb are metals. -
Appearance: C is black. Si is calorie-free-chocolate-brown, Ge is greyish, Sn and Lead are argent white. -
Density: Density increases with an increase in atomic number due to an increase in mass per unit volume down the grouping.
Endeavour yourself:Which of the following group xiv elements is a metal?
Explanation
In that location are mainly 5 elements in the carbon family; carbon, silicon, germanium, stannum and plumbum. Carbon and silicon are non-metals, germanium is a metalloid whereas stannum, plumbum are metals.
-
Melting points and Boiling points: -
Oxidation state: They exhibit +2 and +four oxidation state.
The compounds of Lead in the +iv oxidation state are powerful oxidizing agents since the +2 oxidation country of Pb is more stable due to the inert pair issue.
The compounds in the +ii oxidation country are ionic in nature and the + 4 oxidation state are covalent in nature (Co-ordinate to Fajan'due south dominion).
Try yourself:What is the fajan's rule about?
Caption
The Fajan'south rule is that the compounds in the +ii oxidation state are ionic in nature and the + four oxidation state is covalent in nature, therefore the Fajan'due south rule is about the Oxidation state and their nature of the compounds.
-
Ionisation enthalpy: It decreases from C to Sn. For Lead, information technology is slightly higher than Sn. -
Electronegativity values: The value decreases from C to Pb merely not in a regular manner probably due to the filling of d-orbitals III and Sn and f- orbitals in Pb. -
Catenation: The greater the strength of the element-element bail, the greater is the strength of catenation. C >> Si > Ge = Sn > Pb (catenation). -
Allotropy: All the elements of this grouping except Lead showroom allotropy. -
Valency: All elements exhibit tetra valency. In the case of carbon, 406 kJ mol-1 of free energy is required for the promotion of 2s – electron to 2p. The formation of two extra bonds provides this energy. -
Atomic and ionic radii: Both increase from C to Pb. - Multiple bonding Carbon forms pπ – pπ bonds with itself and with S, N and O. Other elements show a negligible trend of this type due to their large size. Others form dπ – pπ multiple bonds.
Note:In cold countries, white tin changes to grey tin and results in a decrease in density. This is called tin disease or tin plague.
- All members of the group form covalent hydrides. Their number and ease of formation decrease down the group.
- Hydrides of carbon are called hydrocarbons (alkanes, alkenes or alkynes).
- Hydrides of Si and Ge are known as silanes and germanes.
- The only hydrides of Sn and Atomic number 82 are SnH4 (stannane) and PbHfour (plumbane).
- Their thermal stability subtract downward the grouping.
- Their reducing graphic symbol increases downwards the group.
- All the elements requite tetrahedral and covalent halides of the type MX4 except PbBr4, and PbIiv.
- Thermal stability: CX4 > SiX4 > GeX4 > SnX4 > PbX4
- Order of thermal stability with common metals: MFiv > MCl4 > MBrfour > MIiv
- Except CX4 other tetrahalides can be hydrolysed due to the presence of vacant d-orbitals.
Vi4 + 2HiiO → SiO2 + 4HX. - Ease of hydrolysis: SiX4 > GeX4 > SnXfour > PbX4
- Except for C, other elements form dihalides of the blazon MXtwo which are allionic and have higher melting points and humid points, e.yard., SnCltwo is a solid whereas SnCl4 is a liquid at room temperature.
Note:
SnCl2 . 5H2O is chosen bitter of tin and is used as a mordant in dyeing.
- They form two types of oxides. mono-oxides of the blazon MO and dioxides of the type MO2.
Case:CO (neutral) and SiO, GeO, SnO, PbO(all basic)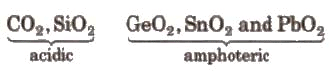
- COii is linear gas at ordinary temperature. Solid CO2 is known as dry out ice or drikold.
- SiOii is solid with a three-dimensional network in which Si is bonded to four oxygen atoms tetrahedrally and covalently. A mass of hydrated silica (SiOtwo) formed from skeletons of minute plants, known as diatoms, is chosen kieselguhr. It is a highly porous textile and is used in the manufacture of dynamite.
Attempt yourself:How many types of oxides do Carbon family form?
Caption
The Carbon family can form ii types of oxides, mono oxides of the type MO like carbon monoxide and silicon monoxide which are all basic, it can likewise found the oxides of the type MOtwo where carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are acidic and the dioxide of Germanium, silicon and plumber are amphoteric.
- The corporeality of carbon present in the world's atmosphere and its chaff is very less. At that place is only 0.02% of carbon in the globe'due south crust. This carbon exists every bit minerals like coal, carbonates and hydrogen carbonates etc. 0.03 % of the carbon exists in the atmosphere of the earth as carbon dioxide.
- Carbon is of utmost importance for our existence and it finds all-encompassing usage in chemistry.
- Because of its indisputable importance, chemistry has been divided into ii branches:
(a) Organic Chemistry: This deals with the various compounds containing carbon.
(b) Inorganic Chemistry: This co-operative deals with compounds that practise not have any carbon content. - Free states (diamond. graphite, coal etc.) and combined states (oxides, carbonates, hydrocarbons etc.)
- Since most of the first members of a grouping have peculiar characteristics and properties. On similar grounds, even carbon behaves differently than the other members of the group. These properties of carbon are very unique.
- We can attribute this behaviour to carbon mainly due to:
(i)Small-scale size of the cantlet
(ii)High electronegativity
(three)High ionization enthalpy
(iv)Unavailability of d-orbital'southward
- Carbon derives a lot of its properties from its small size.
- The compounds that carbon forms are highly stable and this is also because of their small-scale size. Due to its small-scale size, the nucleus effectively holds on to the bonded and non-bonded electrons.
- Carbon exhibits tetravalency. It ways information technology tin can share 4 electrons to complete its octet. Thus, we know it bonds to iv dissimilar monovalent atoms.
- Carbon forms a big variety of compounds with oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, halogens. This results in a different set up of compounds that accept distinctive characteristics and backdrop.
- Carbon has the availability of but s and p orbitals. Therefore, information technology tin hold only 4 pairs of electrons in its valence shell. Thus, we tin can restrict the covalence to four. However, the other elements in the group can hands grow their covalence due to the availability of d-orbitals.
- One of the unique properties of Carbon is its power to form long carbon bondage. Information technology implies that carbon attaches with other carbon atoms to form long carbon chains. This belongings is known as catenation. Sometimes, this chain could exist as large every bit to have a total of 70-80 carbons.
- This gives rise to a variety of complex compounds. Some of the compounds accept a direct carbon concatenation while some others have branched carbon chain or rings.
- The carbon compounds having only a unmarried bond are saturated hydrocarbons. On the other hand, the compounds with the double or triple bond are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- As we movement down the group, the size of the elements increases. This results in decreasing electronegativity. Thus, the propensity to show catenation also decreases. This can be clearly observed from bond enthalpy values.
- The catenation order: C >> Si > Ge >> Sn.
- Additionally, carbon has an boggling capacity to shape pp – pp multiple bonds with itself and with different molecules. This tin also be related to its smaller size and high electronegativity. Some of the examples would include C = C, C° C, C = O, C = S and C° N.
- Equally a matter of fact, the heavier elements don't shape pp – pp bonds. This is mainly because of the reason that their nuclear orbitals are as well vast and diffused to have viable overlapping.
Case: Lead does non indicate catenation.
Q. Give some practical uses of carbon.
Ans. In that location are many important uses of carbon. Some of them are:
- We utilise impure carbon in the form of charcoal (from wood) and coke (from coal) in metallic smelting.
- Graphite is a mutual use in pencils. We also use graphite to make brushes in electric motors and in furnace linings.
- Activated charcoal finds its usage in purification and filtration in respirators and kitchen extractor hoods.
- Industrial diamonds are a mutual tool for cutting rocks and drilling.
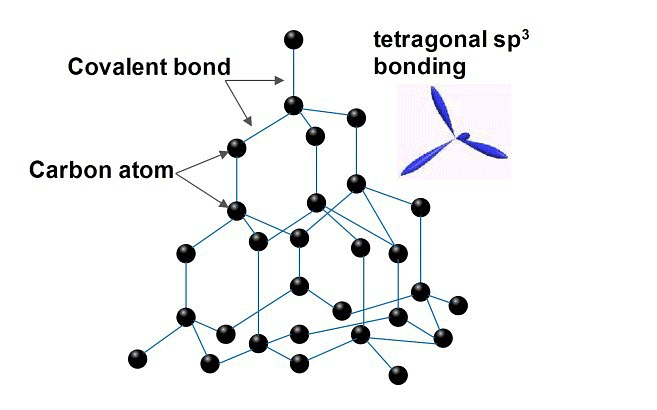
The crystalline forms include:
- Information technology is the hardest and has a iii-dimensional polymeric structure in which the hybridization of C is spiii.
- Information technology is a covalent solid.
- Melting signal = 3650 °C
- Density = 3.51 thou/cm3
- Bad Conductor of heat and electricity.
- It is dark greyness having hexagonal plates, hybridization of each C is sp2.
- It is a good conductor of heat and electricity due to the presence of free electrons.
- It was also known as the black atomic number 82.
- It is a very practiced lubricant.
- Aqua dag: Suspensions of graphite in water.
- Oil dag: Suspension of graphite in oil lubricants.
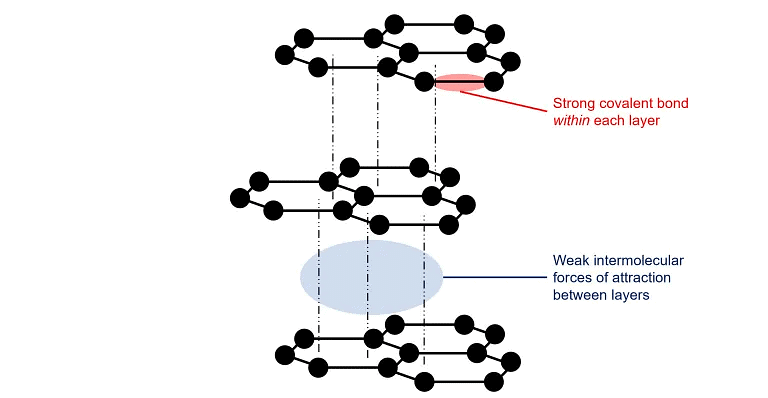
Structure of Graphite
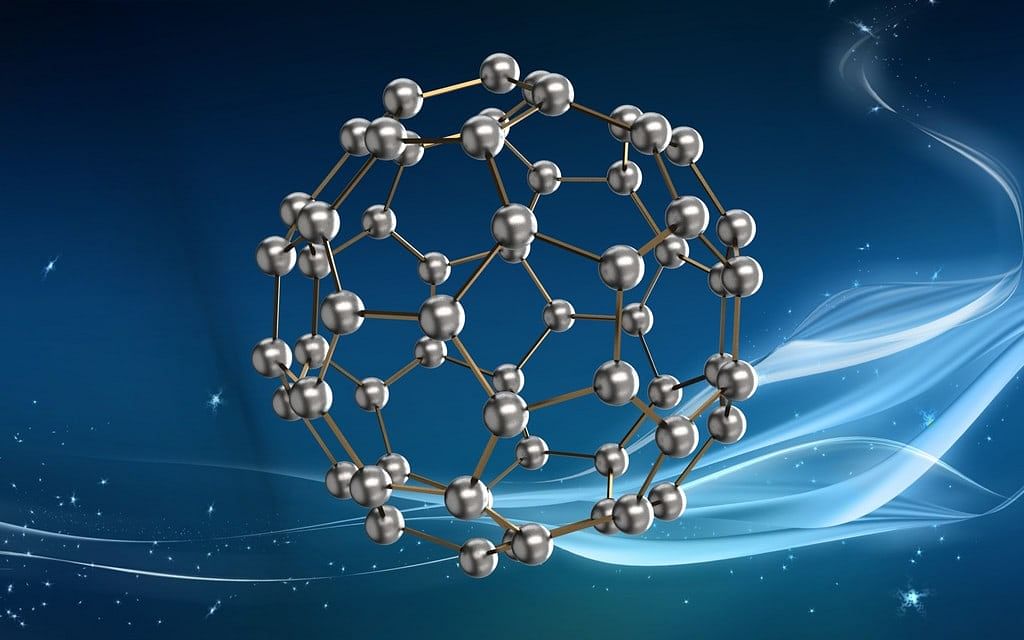
- These are the only pure course of carbon.
- C60 molecule contains 12 5-membered rings and 20 half dozen-membered rings.
- The five-membered rings are connected to six-membered rings while six-membered rings are connected to both five and vi-membered rings.
- These are used in microscopic ball bearings, lightweight batteries, in the synthesis of new plastics and new drugs.

Endeavour yourself:Which of the post-obit allotropes of carbon are hard in nature?
Explanation
The crystalline grade of allotropic carbon is diamond, it is the hardest and has a iii-dimensional polymeric structure in which hybridization of carbon is sp3. It is a covalent solid, melting indicate is 3650-degree centigrade and it is also a bad conductor of oestrus and electricity.
- Coal:The unlike forms of coal are peat (lx % C), lignite (seventy % C), Bituminous (78 % C), Semi Bituminous (83 % C) and anthracite (90 % C). Bituminous is the most common diversity of coal.
- Cokeis obtained by the subversive distillation of coal.
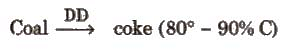
- Charcoal or wood charcoal: It is obtained past heating woods strongly in absenteeism of air. When heated with steam, it becomes more activated. It is used to remove colouring matters and odoriferous gases.
- Os black or brute charcoal It is obtained by destructive distillation of bones in fe retort. Past-products are bone oil or pyridine. It is used as an adsorbent. On burning, it gives bone ash which is calcium phosphate and used in the industry of phosphorous and phosphoric acid.
- Lamp-black Information technology is obtained by burning vegetable oils in a limited supply of air. It is used in the manufacture of printing ink, black paint, varnish and carbon paper.
- Carbon-black It is obtained by burning natural gas in a express supply of air. It is added to a prophylactic mixture for making automobile tyres.
Try yourself:Which of the following is an amorphous allotrope of carbon?
Explanation
Diamond, fullerenes come and graphite are crystalline allotropes of carbon whereas lampblack is an amorphous form of carbon, which is obtained past burning vegetable oils in a limited supply of air and it is too used in the industry of printing ink, blackness pigment, varnish, and carbon paper.
-
Coal Gas:
Preparation:By destructive distillation of coal.
Limerick: H2 = 45 – 55%, Northwardii = 2 – 12%, CHfour = 25 – 35%, CO2 = 0 – iii%, CO = 4 – 11%, O2 = 1 – 1.five%, Ethylene, acetylene, benzene, etc. = 3 – 5 %
Uses: It is used as an illuminant, every bit fuel and to provide an inert atmosphere in the metallurgical processes. -
Natural Gas:
It is found forth with petroleum below the surface of the earth.
Composition: CH4 = sixty – 80 %, Higher hydrocarbons = ii – 12%, C2Hhalf-dozen = 5 – 10 %, CiiiH8 = 3 – eighteen %
Uses: Information technology is used as a fuel. Its partial combustion yields carbon black (reinforcing amanuensis for rubber). -
Oil Gas:
Training:
 Uses: It is used every bit fuel in laboratories in Bunsen burners.
Uses: It is used every bit fuel in laboratories in Bunsen burners. -
Forest-Gas:
Grooming: Subversive distillation of woods gives wood gas (CH4, CiiHvi H2)
Uses: Information technology is used as fuel. -
Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG):
Composition: n-butane + Iso-butane
Uses: It is used as domestic fuel. -
Carbon Monoxide (CO):
Preparation:
It is manufactured in the form of h2o and produces gas.
Properties:
(i) It is a colourless, odourless and well-nigh water-insoluble gas.
(ii) It is a powerful reducing agent.
(iii) CO is used in the extraction of many metals from their oxide ores.
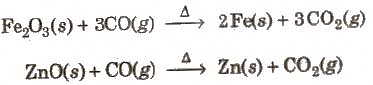
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
Preparation:
(i)
(ii)
(three)
Properties:
(i)It is a colourless and odourless gas.
(ii)With water, it forms carbonic acid.
(three)Photosynthesis
-
Silicates
Silicates are metal derivatives of silicic acid, HtwoSiO3 and can be obtained past fusing metal oxides or metal carbonates with sand. The basic structural unit of silicates is SiO4 4-.
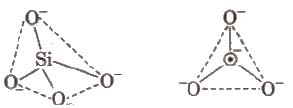
Mica (abrak) is naturally occurring aluminium silicate [KH 2 AI 3 (SiO iv ] 3 or KAI 3 Si 3 O x (OH)2. -
Silicones
The linear, cyclic or cantankerous-linked polymeric compounds containing (R2SiO) as a repeating unit, are known as silicones. They are manufactured from alkyl-substituted chlorosilanes.
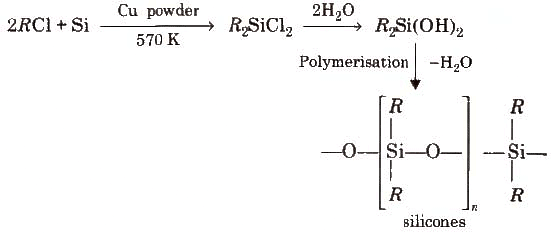 Silicones are chemically inert, water repellent, heat resistant, practiced electrical insulators. These are used equally lubricants (vaseline), insulators etc
Silicones are chemically inert, water repellent, heat resistant, practiced electrical insulators. These are used equally lubricants (vaseline), insulators etc -
Carborundum -
Glass
Coloured spectacles are obtained by adding a sure substance to the molten mass.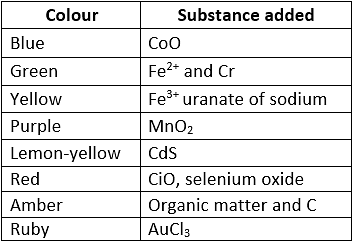 Different Varieties of Glass:
Different Varieties of Glass: 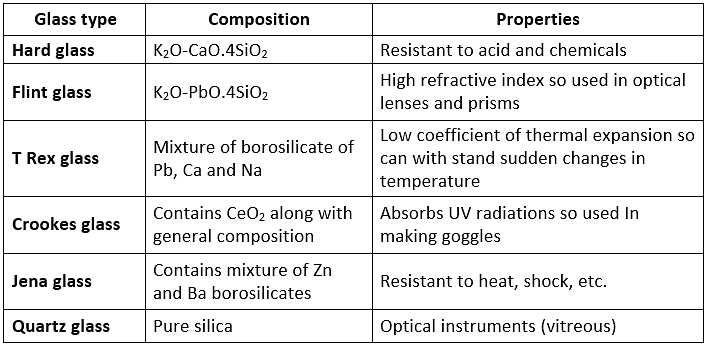 Glass is attacked by HF. This property is used in the etching of glass.
Glass is attacked by HF. This property is used in the etching of glass.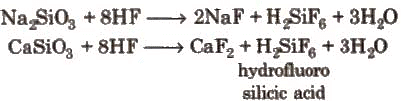
Try yourself:The cross-linked polymer compounds containing silicone which are linear and the circadian are chosen ___________
Caption
The linear, circadian or cross-linked polymer compounds containing RiiSiO, every bit a repeating unit, is known as Silicones. They are manufactured from alkyl substituted chlorosilanes they are chemically inert, water repellent and likewise heat resistant.
-
Chrome yellow (PbCrO4):
It is prepared by adding potassium chromate to lead chromate and is used as a yellow pigment under the proper name chrome xanthous. On treating with alkali, it gives basic lead chromate or chrome red, PbCrOiv.PbO. -
Basic lead carbonate, Pb(OH)2.2PbCO 3
It is also known every bit white atomic number 82 and is prepared by adding sodium carbonate solution to whatever lead salt.
3Pb(NO3)2 + 3Na2CO3 + H2O → Lead(OH)2.2PbCOthree + 6NaNO3 + COiiInformation technology is used equally white paint. The disadvantage of using white atomic number 82 in paints is that it turns black by the action of H2S of the atmosphere.
Notation:
Pb poisoning is chosen plumbosolvency which increases in the excess of nitrates, organic acids and ammonium salts.
Try yourself:Which of the following is non a component of glass?
Explanation
Glass is a transparent or translucent amorphous substance, which is obtained by fusion of sodium carbonate or sodium sulphate, calcium carbonate and sand (which is also known every bit silica), the general formula of glass is Na2O.CaO.6SiOii
The document Group xiv (Carbon Family) Notes | Study Chemistry Class 11 - NEET is a office of the NEET Grade Chemistry Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
Source: https://edurev.in/studytube/Group-14--Carbon-Family--Properties-and-Compounds-/dc5a81e6-19cf-4fc3-97e8-c2ec461926be_t
Post a Comment for "Why Is Group 14 Called the Carbon Family"